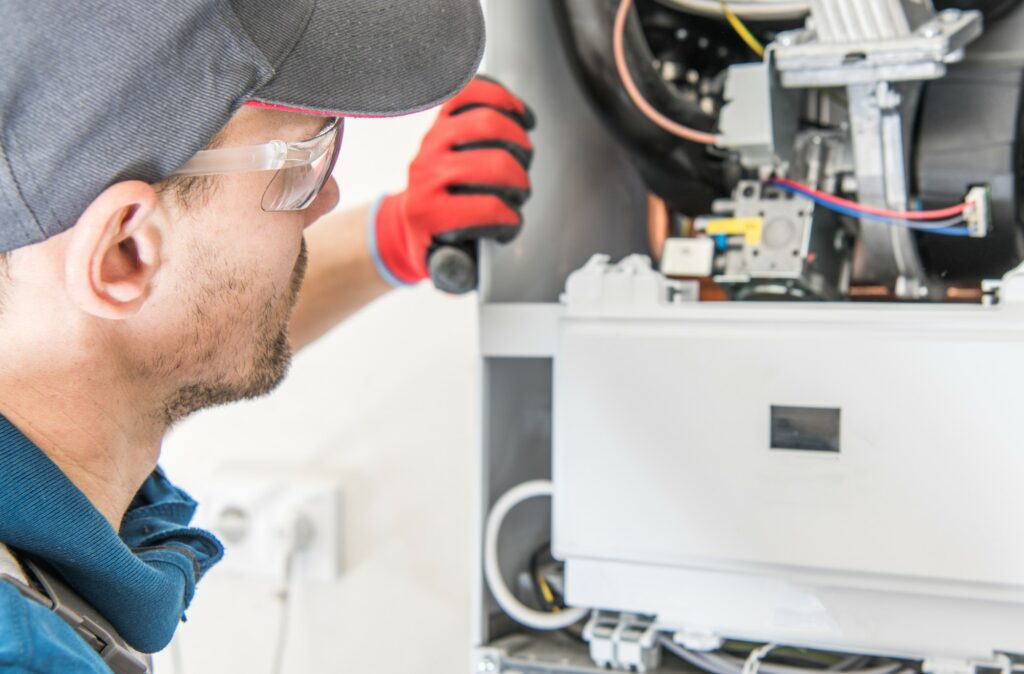
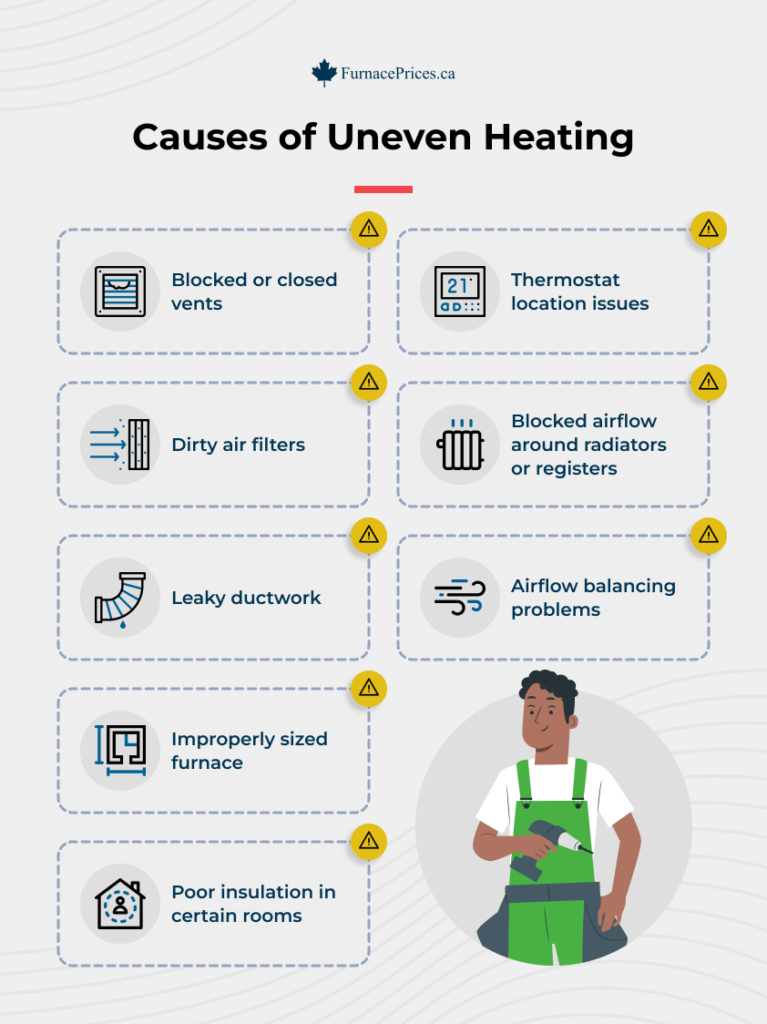
1. Your Heating System Is Making Unusual Noises
Banging Noises
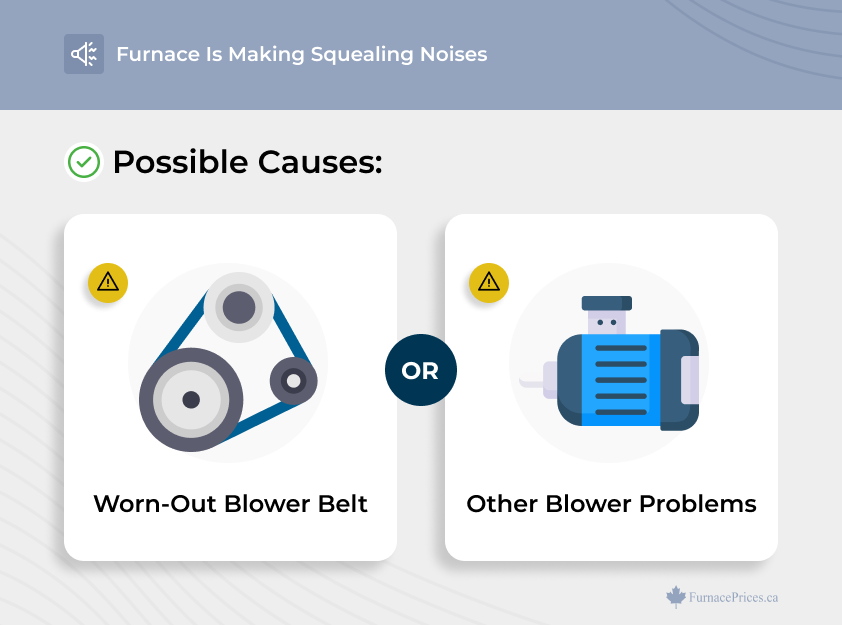
Squealing Noises
Rattling Noises
Scraping Noises
2. Your Carbon Monoxide Alarm Is Going Off

According to the injury prevention organization Parachute, “carbon monoxide is a leading cause of unintentional poisoning deaths in Canada and North America,” and it accounts for more than 300 deaths and 200 hospitalizations annually.
3. Your Heating System Is Short Cycling
See, short cycling causes two problems: 1. it puts unnecessary wear and tear on the unit, causing it to die before its time, and 2. it causes the unit to use more energy than it would otherwise, resulting in higher energy bills. Both problems result in a loss of money.
What causes short cycling? In some cases, it occurs due to an improperly sized unit. In other cases, it’s a result of dirty sensors or a malfunctioning thermostat.
Regardless, if you’re experiencing this problem, you need to call up your local emergency furnace repair technician. They’ll determine the problem’s source and then take all necessary action in order to fix it.
4. You’re Not Receiving Hot Air
5. A Yellow Pilot Light
If your furnace has a pilot light, the flame should be blue and burn strong and consistently.
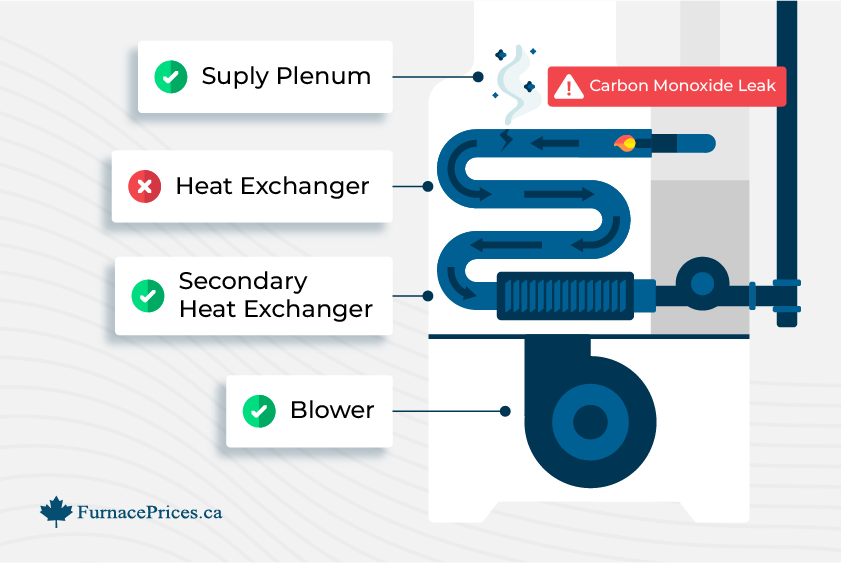
A yellow or orange flame indicates the gas isn’t burning hot enough. This could be from dirty burners, not enough oxygen, malfunctioning gas valve or heat exchanger, or incorrect gas pressure.
And here’s why it’s dangerous: A yellow flame can mean incomplete burning, which can mean the furnace is leaking carbon monoxide and needs an emergency furnace repair.
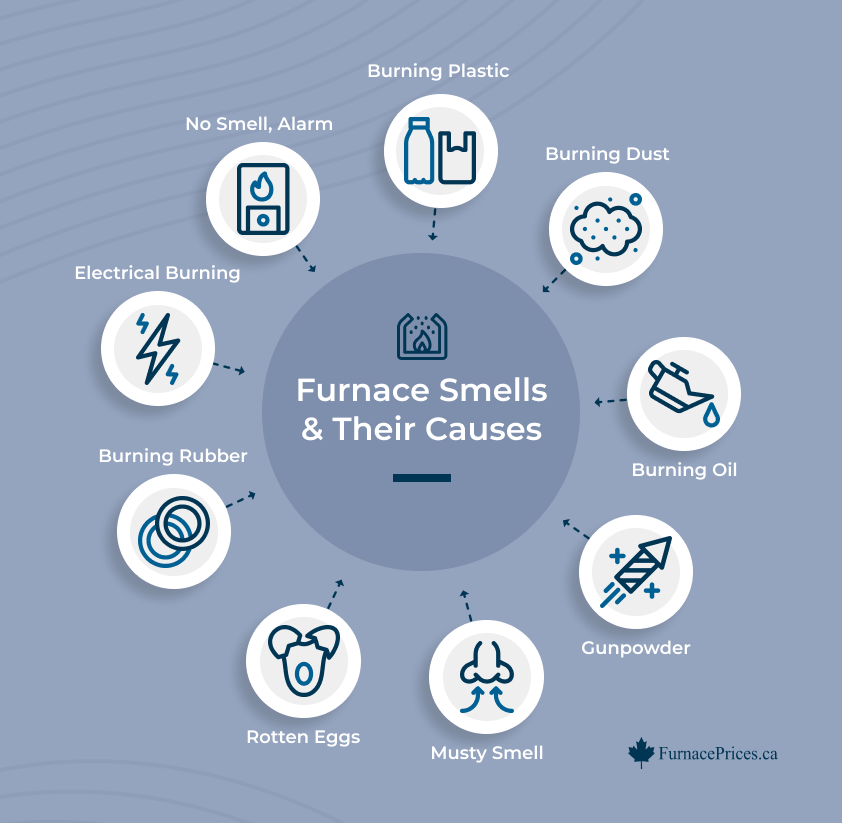
6. Unpleasant Smells

Lots of furnace problems can generate weird smells, especially burning smells, such as:
- Burning plastic
- Rotten eggs
- Burning rubber
- Burning dust
- Electrical burning
- Smoky smell or burning oil
The specific smell can give you an idea of what might be wrong. Burning oil and rotten egg smells are particularly worrisome.
Burning oil can indicate a malfunctioning burner or improper combustion, while rotten eggs can indicate a gas leak. Call an emergency furnace repair technician immediately if you notice these smells.
7. Furnace Fan/Blower Keeps Running
When a furnace fan (aka blower) keeps running, there may be an easy fix: Switching the thermostat from On to Auto. It could also mean you need to change/clean the furnace filter.
However, if that isn’t the problem, it could mean a faulty thermostat or problem with the fan limit switch.
Further, there could also be a wiring problem, or the furnace could be overheating, and that means you need an emergency furnace repair.
8. Furnace Won’t Turn On or Stay On
A furnace that won’t come on or stay on can have many problems, including with the power supply, thermostat, flame sensor, control board, and many more. In fact, the most common culprit is a dirty filter.
You can try changing the filter, but if that doesn’t fix the problem, call a local HVAC technician for an emergency furnace repair. There could be a serious and potentially dangerous problem with the furnace, like it’s overheating.
Furnace Troubleshooting Wizard
Why You Shouldn’t Delay an Emergency Furnace Repair
Delaying an emergency furnace repair can have consequences for your health and safety, furnace lifespan, home comfort, wallet, and more.
In terms of health and safety, putting off a serious furnace repair could cause/exacerbate a gas leak, carbon monoxide leak, or fire. Depending on what the problem is, it could also lead to poor indoor air quality in the home.
What’s more, ignoring a problem could make it worse, resulting in a shorter lifespan for the furnace or possibly a complete breakdown, which could leave your family without heat.
It’s also a lot cheaper to take care of minor maintenance than to pay for major repairs or to replace a furnace.
Another way it could cost you more in the long run is with increasing energy bills. If your furnace isn’t’ operating at peak efficiency, it’s going to cost more to heat your home.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Furnace Emergencies

Regular maintenance and inspections are the most effective ways to keep your furnace in good working order and prevent the need for an emergency furnace repair.
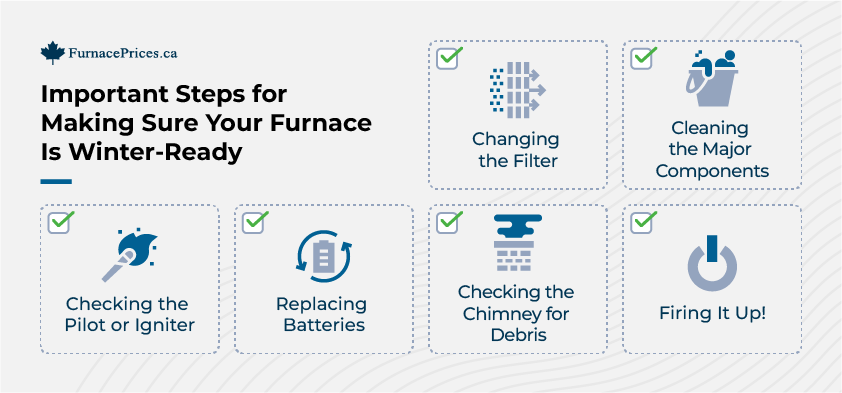
Annual inspections and most maintenance should be left to a local HVAC professional, but there are some maintenance steps you can take care of yourself, such as:
- Changing the filter
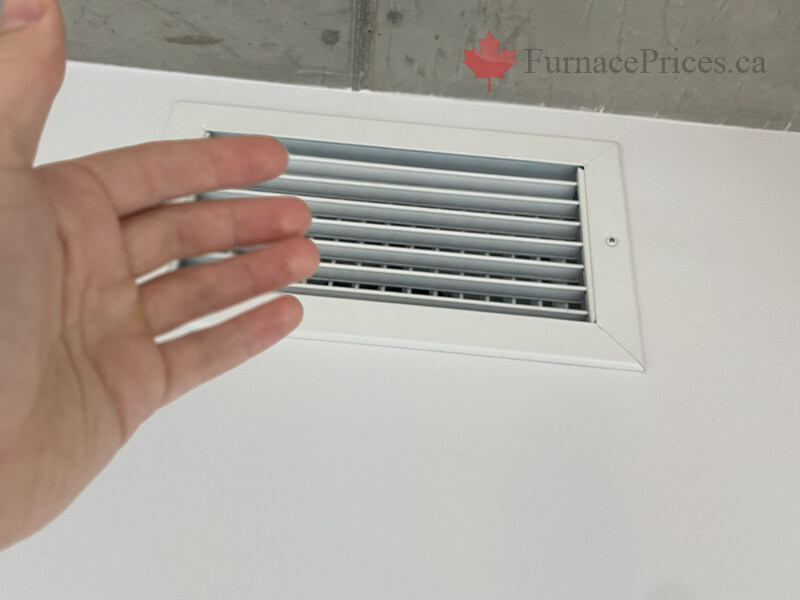
- Keeping vents and ducts clean and clear
- Vacuuming/cleaning/inspecting major components
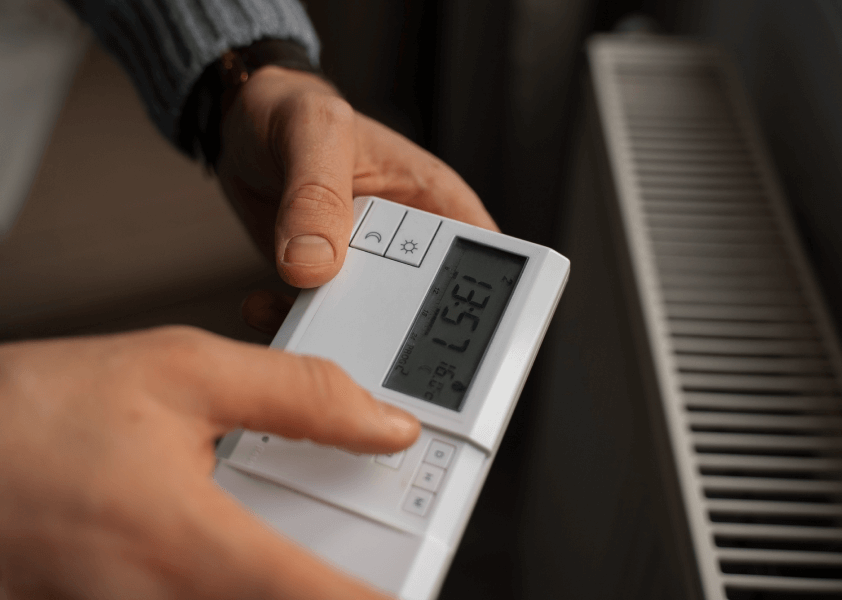
- Making sure the thermostat is working properly
- Lubricating moving parts
- Checking the pilot light