Buying a new furnace is a big decision because there’s so much choice on the market these days, including different brands, makes and models, available technologies, furnace types, and efficiency ratings.
But one of the most important things you’ll need to know before you buy a furnace is what size you need for your space.
Sizing a furnace isn’t just about calculating the square footage of your home. There are lots of things you have to account for when sizing a furnace. Today we’ll explain what those factors are, explore why it’s important to size a furnace properly, and talk about how you can get a furnace that’s the right size for your space, your climate, and your comfort needs.
Furnace Size & BTU Calculator
➤ Try our new Furnace Sizing & BTU Calculator to get an instant estimate for your home!
Why Furnace Size Is So Important
It might be tempting to buy a smaller furnace to save money on the purchase price or to buy a larger one to maximize space-heating, but furnaces are like Goldilocks’ porridge: you need one that is just right, for your home.
A furnace that’s too big will cycle irregularly. This is bad because it will create hot and cold spots throughout the house, impact efficiency, increase maintenance, and reduce the lifespan of the furnace.
A furnace that’s too small will run continuously and still won’t be able to keep your home at a comfortable temperature. The increased workload will also raise your energy bills, create maintenance problems, and cut the life of the furnace short.
Furnace Size Can Maximize Energy Efficiency
Another problem with having a furnace that’s the wrong size is that it will negatively impact the efficiency of the heating system.
The AFUE (annual fuel utilization efficiency) of a furnace is calculated based on normal operation. When a furnace runs continuously or irregularly because it’s not the right size, then you won’t get the efficiency rating you paid for, and that will result in more energy use and higher heating bills.
To ensure your furnace operates at the efficiency level it’s supposed to, it has to be sized properly for your home.
How Furnace Size is Measured
When you talk about furnace size, you’re not actually talking about the physical dimensions of the unit. Rather, a furnace’s size is related to its heating output, and how much heat it can generate.
Furnace output is usually measured in British thermal units (BTUs) per hour. A BTU is a measurement of energy, and specifically the amount of energy required to increase 1 pound of water by 1 F.
A bigger furnace, such as one with an output of 120,000 BTUs per hour, will generate enough heat for a larger space. A smaller furnace will have a smaller BTU capacity, such as 40,000 BTUs per hour, and be suitable for a smaller space.
Some manufacturers have started measuring furnace size in MBH instead of BTUs. MBH is one thousand BTUs per hour, so you’re still working with the same measurement: 60 MBH is 60,000 BTUs.
Furnace Sizing Starts with Square Footage
One of the biggest things that will impact your furnace size is the size of your home, and specifically how many square feet of space need to be heated.
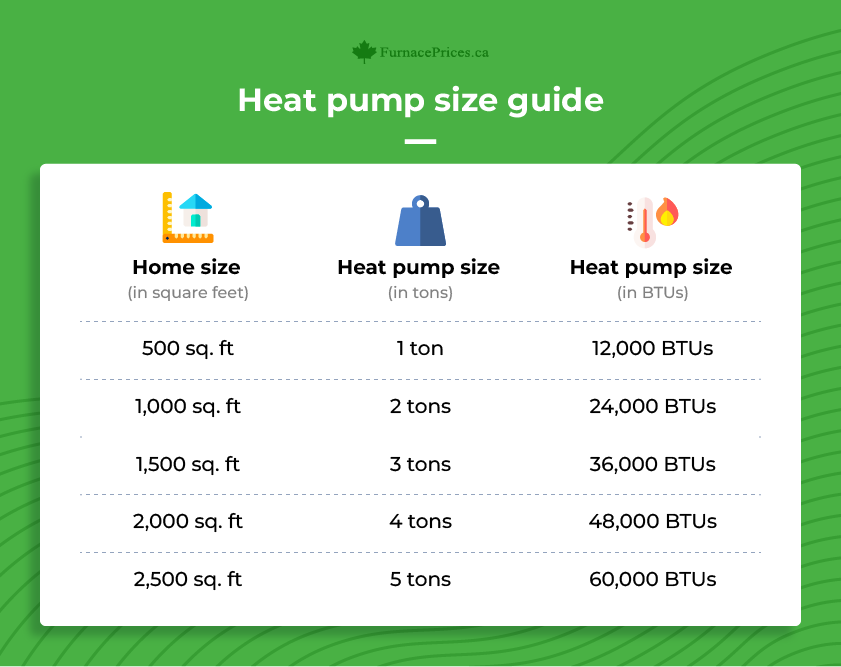
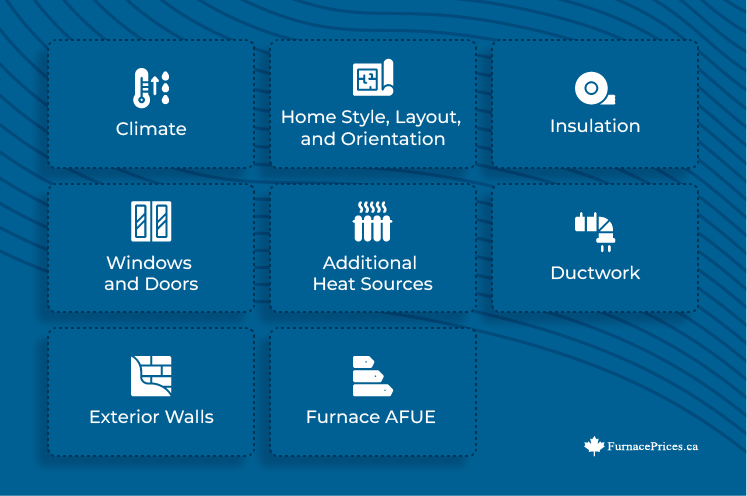
You can use the square footage to get an idea of what size range you should be looking at for your new furnace. From there, however, there are plenty of things that can impact the size furnace you need, including:
- The climate where you live
- The style and orientation of your home
- How many exterior walls you have
- The quality and thickness of your insulation
- The number of windows and doors, and their age
- Furnace efficiency
- The state of your ductwork
You’ll have to factor in all these elements, along with square footage, to accurately calculate furnace size.
Factors Other Than Square Footage that Impact Furnace Size
Climate
Canada is a rather large country, and the climate in winter can vary drastically depending on where you live. The climate will also help to determine what size furnace you need.
For example, a 2,000 square foot home in Ottawa would require a larger furnace than that same home in Victoria because Ottawa winters are so much colder.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*



Home Style, Layout, and Orientation
The design of your home is important to consider when sizing a furnace because there are so many little things that can impact heating requirements.
Orientation is one of them. South-facing homes get more sun, and in winter you can take advantage of this by letting in the light and allowing the sun to warm your home. In other words, south-facing homes might be able to get away with smaller furnaces than homes that are shaded.
The number of floors in your home will also impact BTU requirements, but maybe not in the way you think. A 1,000-square-foot home with a single floor will need a slightly bigger furnace than a 1,000-square-foot home with two floors because the second floor actually provides insulation, thereby reducing heating requirements.
Your floor plan can also affect furnace size because open-concept homes have fewer interior walls to hold heat compared to homes with lots of isolated rooms, and this can mean you need a larger furnace.
Furthermore, certain features like sliding doors or sunrooms may leak heat more readily and therefore may increase overall heating requirements, especially in that part of the home.
Insulation
Insulation is an important tool that can increase the efficiency of your home. Homes that are well-sealed and have thick insulation are more efficient, and efficient homes can typically get away with smaller furnaces.
Insulation isn’t just important in the walls: your attic, crawlspace or basement, and roof all need to be insulated to prevent heat loss.
Windows and Doors
Windows, skylights, and doors can be notorious for leaks and drafts, especially older ones that aren’t energy-efficient and properly sealed. The more glass and entryways you have, the more BTUs you’ll need to compensate for the heat loss.
By contrast, if you don’t have a lot of these features, they’re very small, or they’re well-insulated and energy-efficient, then a slightly smaller furnace might be sufficient.
Additional Heat Sources
Some homes have wood stoves, gas fireplaces, and other secondary heat sources that can reduce the demands on a furnace. If you have additional heat sources that you use regularly in the winter, then you won’t need a furnace with as many BTUs of heating output.
Ductwork
Like with windows and doors, leaky ductwork can increase heating demands throughout your house and increase the furnace size you need, along with increasing your energy bills.
It might be worthwhile to perform a visual inspection of your ductwork to see if there are any problem areas. By fixing leaks, you can improve the overall efficiency of your home and your heating and cooling systems.
Exterior Walls
Homes with fewer exterior walls have less exposure to the elements, and will likely have lower heating requirements. This can include:
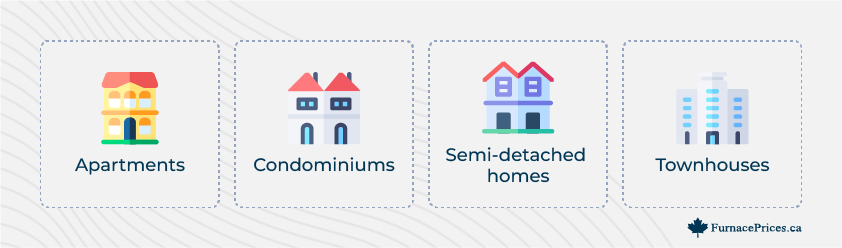
- Apartments
- Condominiums
- Semi-detached homes
- Townhouses
Furnace AFUE (its energy efficiency rating)
We already mentioned how size can impact AFUE, but the AFUE of the furnace can also impact the size you need.
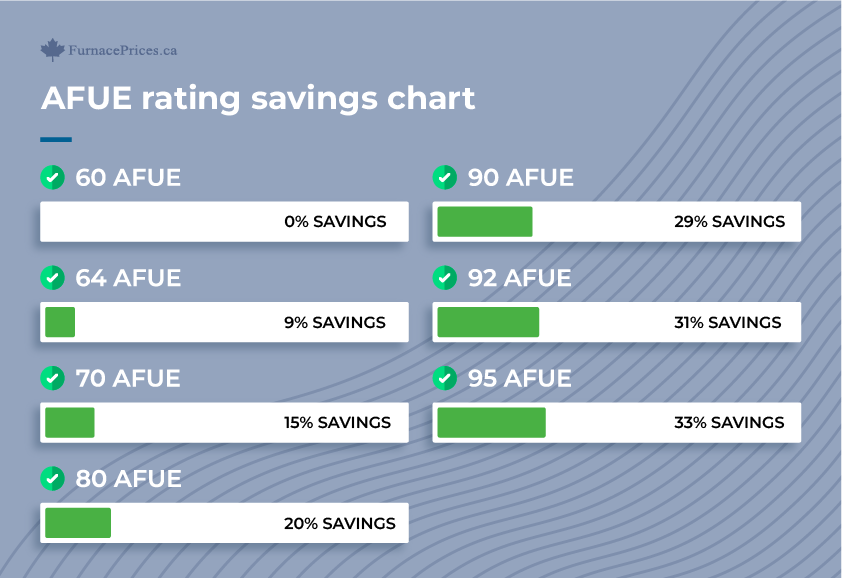
Let’s use a 100,000 BTU furnace as an example. At 100 percent efficiency, that furnace would indeed generate 100,000 BTUs of heat per hour. However, if the AFUE is only 90 percent, then that same furnace will only generate 90,000 BTUs of heat per hour.
The take-home here is this: the lower the efficiency rating, the larger the furnace will need to be.
You will pay more for a higher efficiency model, but you’ll also be able to get away with a smaller furnace, and that will offset some of the cost. Furthermore, you’ll save more on energy bills in the long run with a high-efficiency furnace.
How to Estimate Furnace Size Based on Square Footage
We’ve already talked about the myriad factors that can impact furnace size, but you can get a basic estimate using the square footage of your home.
While you shouldn’t use this calculation to make a final decision about furnace size, you can use it to get an idea of the size range to look at when you’re shopping for a new model.
The general rule of thumb is that you need between 30 and 60 BTUs per square foot, depending on your climate.
Climate zones can help you determine how many BTUs per square foot you need. You can find more information about climate zones and insulation requirements from the North American Insulation Manufacturers Association.
As a general guideline, the Vancouver region and similar nearby locations would be considered mild climates. The prairies and other northern regions would be considered cold climates. And most of the rest of the country like Southern Ontario and the Maritimes would be considered moderate climates.
Furthermore, many homeowners in colder climates opt to have dual furnaces, especially for larger homes.
Here’s a list of general BTU capacity requirements you can use as a starting point to estimate furnace size:
| Square Footage | Furnaces Size for Mild Climates (30) | Furnace Size for Moderate Climates (45) | Furnace Size for Cold Climates (60) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,000 | 30,000 BTUs | 45,000 BTUs | 60,000 BTUs |
| 1,200 | 36,000 BTUs | 54,000 BTUs | 72,000 BTUs |
| 1,500 | 45,000 BTUs | 67,500 BTUs | 90,000 BTUs |
| 1,800 | 54,000 BTUs | 81,000 BTUs | 108,000 BTUs |
| 2,000 | 60,000 BTUs | 90,000 BTUs | 120,000 BTUs |
| 2,200 | 66,000 BTUs | 99,000 BTUs | 132,000 BTUs |
| 2,500 | 75,000 BTUs | 112,500 BTUs | 150,000 BTUs |
| 2,800 | 84,000 BTUs | 126,000 BTUs | 168,000 BTUs |
| 3,000 | 90,000 BTUs | 135,000 BTUs | 180,000 BTUs |
Let’s look at an example of how these estimates can help you.
Say you live in a cold climate like Winnipeg in a home that’s 1,800 square feet. The chart would indicate you need a furnace that’s around 108,000 BTUs. But let’s say your home is older, doesn’t have a lot of insulation, and has drafty windows. That could add an additional load to your heating requirement, so you might want to look at furnaces between 110,000 and 130,000 BTUs.
But then say you recently upgraded the insulation, installed energy-efficient windows and doors, and were looking at a furnace with an efficiency rating around 99 percent. In that case, you might want to look at furnaces between 85,000 and 100,000 BTUs instead.
These are just examples with estimated numbers to give you an idea of how the additional factors will change the furnace size you need.
Getting a Furnace Professionally Sized
The best way to ensure your furnace is the right size for your home is to have an evaluation from a professional HVAC expert.
An experienced HVAC technician will be able to accurately calculate the square footage of your home, factor in all the other elements that can impact furnace size, and give you a precise BTU capacity for your furnace.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*











