Electric furnaces are increasingly becoming a popular choice amongst Canadians. Why? They’re reliable and run clean without relying on fossil fuels.
In this guide, we will discuss the top electric furnace brands available in Canada, their costs, and reviews. We will also compare the advantages and disadvantages of electric furnaces over their gas counterparts.
What Is an Electric Furnace and How Does It Work?
An electric furnace is a heating system that uses electric heating elements to warm air distributed throughout a building.
Electric furnaces have been part of home heating solutions for many years. Their extensive history dates back to their emergence in the early 18th century.
The main difference between an electric and a gas furnace is their heat source and operation method. Unlike gas furnaces that burn natural gas or propane to generate heat, electric furnaces convert electricity directly into heat through heating elements made of metal coils.
Canada’s government advises an electric furnace should not have an input rate of more than 65.92 kW (225,000 Btu/h).
Heating and Cooling With an Electric Furnace
While an electric furnace excels at heating, integrating it with an air conditioning unit allows for a unified heating and cooling system.
Split Systems are the solution for heating and cooling, featuring an outdoor condenser and an indoor air handler (your furnace). This setup enables the furnace to circulate heated and cooled air, depending on the season, without directly cooling the air.
Electric Furnace Sizes
Here’s the electric furnace output needed for different home sizes across various climate zones.
| Home Size (sq ft) | Mild Climate BTU/hr | Moderate Climate BTU/hr | Cold Climate BTU/hr |
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 | 18000 | 27000 | 36000 |
| 1200 | 36000 | 54000 | 72000 |
| 1800 | 54000 | 81000 | 108000 |
| 2400 | 72000 | 108000 | 144000 |
| 3000 | 90000 | 135000 | 180000 |
The climate zones are categorized as mild, moderate, and cold, each requiring a different BTU per square foot estimate:
- Mild climates: Approximately 30 BTUs per square foot
- Moderate climates: Approximately 45 BTUs per square foot
- Cold climates: Approximately 60 BTUs per square foot
Electric Furnace Heating Process — Step-by-Step

Electric furnaces work like a hair dryer. The process of an electric furnace works as follows:
- When the home temperature drops below the thermostat setting, it sends an electrical signal to the furnace to start heating.
- The signal causes relays within the furnace to close, enabling electricity to flow to the heating elements.
- The heating elements resist the electrical flow, causing them to heat up rapidly.
- The furnace’s blower motor activates to draw room-temperature air into the furnace through the return air ducts.
- This air moves over the hot heating elements, absorbing heat and increasing temperature.
- The blower forces the heated air through the furnace’s heat exchanger into the home’s ductwork.
- The ductwork distributes the warm air throughout the house via vents.
- Once the indoor temperature matches the thermostat setting, the thermostat signals the furnace to stop heating.
- The blower may continue to run briefly, pushing the remaining warm air into the house to use residual heat efficiently.
- The system goes into standby mode until the temperature drops again, restarting the cycle as needed.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*



Parts of an Electric Furnace
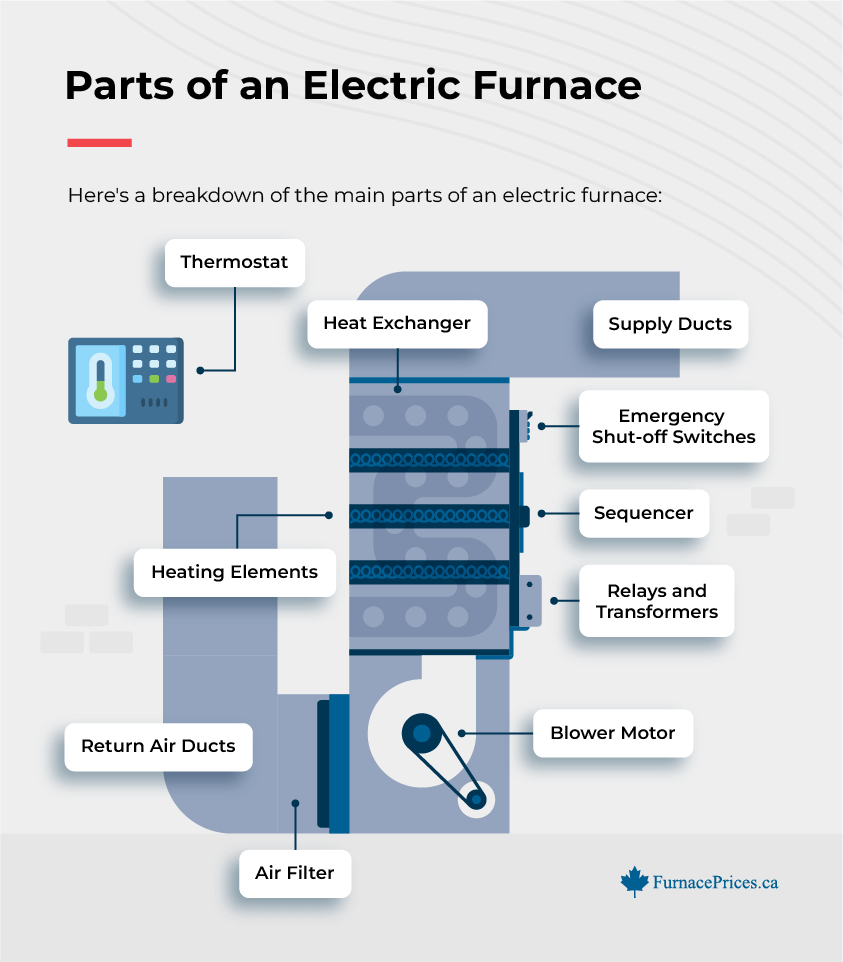
Electric furnaces convert electricity directly into heat using heating elements. On the other hand, gas furnaces burn fuel to create heat, requiring additional components like a gas valve, burner assembly, and exhaust flue to manage combustion and venting safely.
Here’s a breakdown of the main parts of an electric furnace and their functions:
- Thermostat: Controls the indoor temperature by signaling the furnace to heat up or shut down, maintaining your desired comfort level.
- Heating Elements: The primary source of heat in an electric furnace. These elements (made of nickel-chromium) heat up as electricity flows through them.
- Blower Motor: Circulates warm air throughout your home and evenly distributes air for consistent warmth.
- Air Filter: Cleans the air passing through the furnace, improving your home’s air quality by trapping dust and other particles.
- Heat Exchanger: Safely contains the heating process, ensuring only clean, warm air is circulated into your living spaces.
- Return Air Ducts: Channels that return cooler air from the house to the furnace for reheating, crucial for efficient air circulation.
- Supply Ducts: Distribute the heated air from the furnace throughout your home to maintain comfortable temperatures.
- Sequencer: Controls the order in which heating elements activate, ensuring balanced heating and electrical load management.
- Relays and Transformers: Manage electrical connections and power distribution to the heating elements and blower motor, ensuring safe operation.
- Emergency Shut-off Switches: Provide a safety mechanism to turn off the furnace immediately if a malfunction is detected, preventing potential hazards.
Best Electric Furnace Brands
Not all HVAC brands carry electric furnaces, but there are a few reputable brands that do. Here’s a look at some of the top brands offering electric furnaces:
Goodman
Goodman owns and manufactures the Direct Comfort brand, which is available exclusively online. Direct Comfort electric furnaces are less expensive than Goodman’s despite having the same manufacturing process and warranty conditions.
The heating capacity of Goodman electric furnaces spans from 10,240 to 68,240 BTUs. They have a lifespan of 15 to 30 years. However, there may be a slight decrease in efficiency after the 15-year mark. The price range can be anywhere from $3,600 to $5,000 (including installation)
Read also: Goodman Furnace Review & Buying Guide.
Trane
Trane is another brand that offers electric heating solutions through a different product line: wall-mounted electric unit heaters. Trane units are designed for those seeking efficient, space-saving heating options, and the range offers heaters with capacities from 5,119 to 16,380 BTUs per hour.
They have a lightweight design, with all units weighing less than 30 pounds. Trane offers a broad selection of pre-engineered, factory-installed control options. This means a smoother, more straightforward setup process for homeowners and installers alike.
York
York electric furnaces caters to those on a tight budget, offering units priced between $1,200 to $2,300 or $2,600 to $7,400 with installation included. This brand is affordable for homeowners needing efficient heating without a hefty investment.
While York may not offer the most advanced features on the market, its electric furnaces are reliable and get the job done, making them a practical option for everyday heating needs.
York manufactures all residential HVAC products in Wichita, Kansas.
Dettson
Dettson distinguishes itself in the electric furnace market as the sole manufacturer offering modulating and 2-stage furnaces with capacities at the lower end of the spectrum, specifically 15 kBTU and 30 kBTUs.
The company’s Chinook line introduces further versatility with its capability to be powered by propane with the help of a conversion kit.
Dettson supports its products with a 10-year warranty on parts for residential applications.
Winchester
Winchester positions itself within the electric furnace market with its forced air furnaces, priced between $1,200 and $1,400. The brand offers a standard 5-year limited warranty on parts.
Notably, some units from Winchester come equipped with a maintenance-free adjustable speed ECM (Electronically Commutated Motor) constant torque blower. This feature is particularly beneficial as it supports 2 to 3.5-ton air conditioning and heat pump applications.
How Much Does an Electric Furnace Cost in Canada?
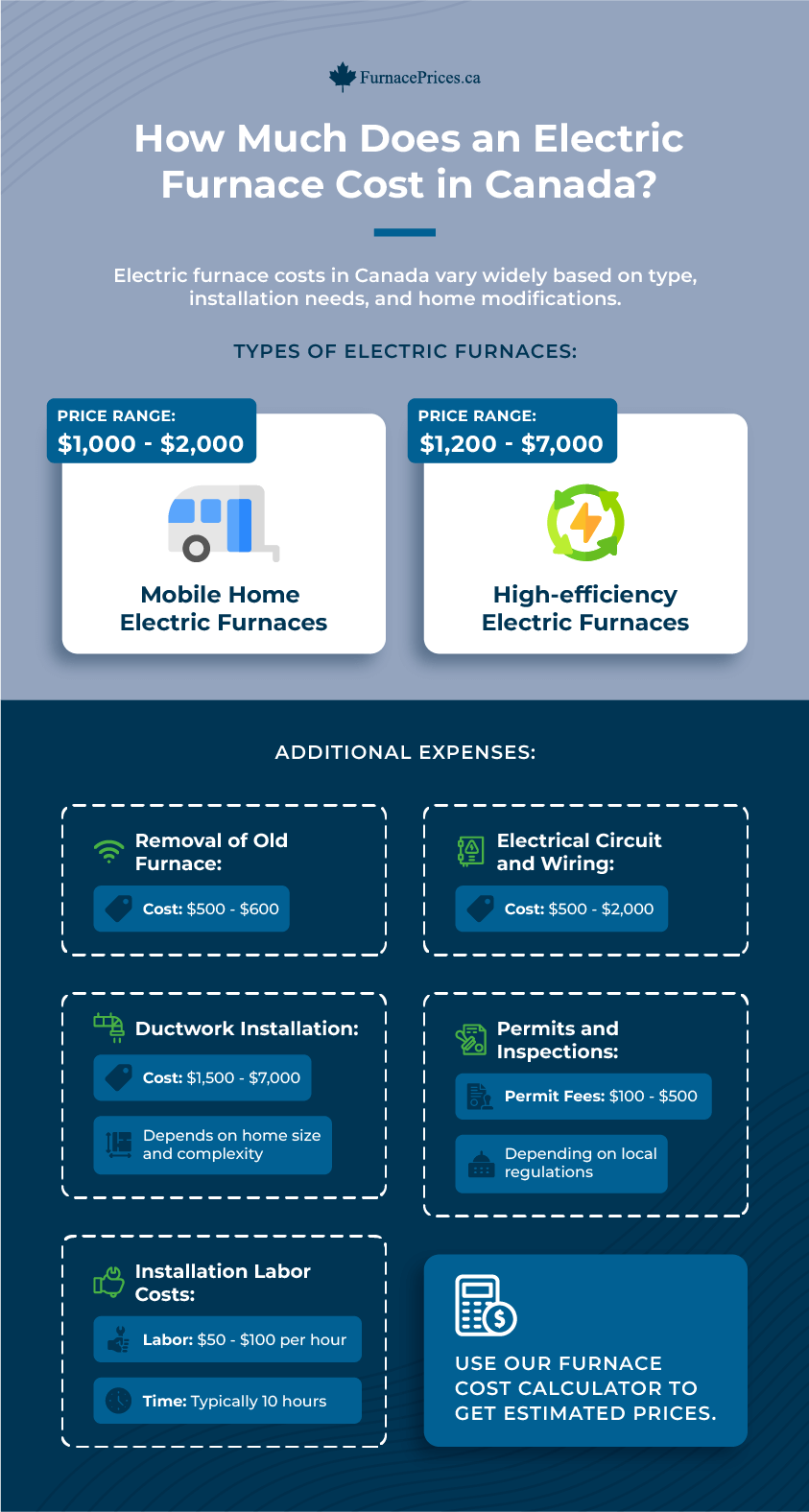
The cost of an electric furnace in Canada can vary widely depending on the type of furnace, installation requirements, and additional upgrades or modifications needed for your home.
- Mobile Home Electric Furnaces: These are typically priced between $1,000 and $2,000. They are designed specifically for compact spaces within mobile homes.
- High-efficiency Electric Furnaces: For those looking for more energy savings, high-efficiency models range from $1,200 to $7,000.
Use our furnace cost calculator to get estimated prices.
Here’s a breakdown of the expenses you might encounter:
Removal of Old Furnace
If replacing an existing furnace, the removal cost usually falls between $500 and $600.
Ductwork
If your home doesn’t have ductwork, installing it can cost between $1,500 and $7,000. The price depends on the installation’s complexity and your home’s size. If your home already has ducts installed, they may still need cleaning, which might cost up to $500.
Installation Labor Costs
Installing an electric furnace involves labor costs ranging from $50 to $100 per hour. The installation process typically takes around 10 hours, depending on the job’s complexity.
Electrical Circuit and Wiring:
Upgrading your electrical system to handle the new furnace can cost between $500 and $2,000 if additional amperage is needed. This ensures your home’s electrical system can safely support the furnace’s operation.
Permits and Inspections
Some localities require permits and inspections for new furnace installations. These permit fees can range from $100 to $500, depending on your area’s regulations.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*



Gas vs. Electric Furnace Operational Cost
Although electric furnaces are 100% efficient, the cost of electricity compared to gas can make them seem more expensive to operate.
For example, producing the same amount of heat might cost about 10 times more with an electric system than with a gas system in some areas.
Generally speaking, the electric furnace’s monthly operating cost can exceed $500 or even $1,000, based on a usage of 9 hours per day at a power consumption rate of 18000 watts and an electricity price of $0.192 per kWh (National Canadian Average).
However, this doesn’t mean electric furnaces are a bad choice. Electric furnaces are a viable option in areas where gas is unavailable or if you’re looking for a safer, simpler heating solution without venting exhaust gasses.
To make electric heating more affordable, consider these strategies:
- Energy Efficiency Upgrades: Improving your home’s insulation and sealing leaks can significantly reduce the amount of heat needed, making electric heating more cost-effective.
- Time-of-Use Rates: Some utilities offer lower electricity rates during off-peak hours, which can make electric heating more economical.
- Utilize Solar Panels: If you want a long-term strategy to reduce electric heating costs, consider investing in solar panels.
If you’re still concerned about the higher operational costs of electric heating, heat pumps can be a compelling alternative. They work by transferring heat from the outside air into your home during the winter, and they can achieve efficiency rates of over 300%.
When Should I Consider an Electric Furnace?

Electric furnaces can be more expensive than gas furnaces due to higher energy costs. However, there are several factors to consider that make an electric furnace the right choice for you.
- Availability of Utilities: If natural gas is not readily available in your area (parts of Newfoundland and Labrador or remote communities in the territories), an electric furnace becomes a practical choice. In regions where connecting to a gas line is not feasible or overly expensive, electric heating offers a viable alternative.
- Environmental Considerations: For Canadians prioritizing a lower carbon footprint, electric furnaces are attractive, especially in provinces like Quebec, British Columbia, and Manitoba, where a significant portion of electricity is generated from renewable sources like hydroelectric power.
- Installation and Maintenance Costs: Generally, electric furnaces are cheaper to install than gas furnaces. They don’t require gas lines or venting systems, which can reduce initial installation costs.
- Safety: Electric furnaces eliminate the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning and gas leaks, offering a safer alternative for your home. If safety concerns are paramount for you, this might tilt the balance in favor of electric heating.
- Cost of Electricity vs. Gas: This is a crucial consideration. In provinces where electricity costs are relatively low, such as Quebec, or where gas prices are higher, the operational costs of an electric furnace might be comparable to gas heating.
- Future Plans: If you’re considering transitioning your home to be more energy-efficient or installing solar panels, an electric furnace could integrate well with these future upgrades.
Things to Consider While Choosing an Electric Furnace
There are several key factors you’ll need to consider to ensure you get a system that meets your heating needs efficiently and cost-effectively.
Square Footage
The size of the furnace, measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units), should match the area to be heated.
| Square Footage | BTUs | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 1,000 | 40,000 | $700–$3,000 |
| 1,000–1,500 | 40,000–55,000 | $1,000–$3,500 |
| 1,500–2,000 | 50,000–70,000 | $1,200–$4,000 |
| 2,000–2,500 | 70,000–90,000 | $1,700–$4,500 |
| 2,500–3,500 | 90,000–100,000 | $1,900–$5,000 |
Remember that the cost can vary due to factors like furnace efficiency, brand, and installation complexities.
CFM Rating
When selecting an electric furnace, you’ll come across different models based on their ratings of CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute). CFM measures how much air the furnace blower can move each minute.
Here’s a simple breakdown to help you understand what each CFM rating means for your home:
| Furnace CFM | Accommodates Airflow (in tons) |
|---|---|
| 1200 CFM | 1.5 to 3 tons |
| 1600 CFM | 3.5 to 4 tons |
| 2000 CFM | 4 to 5 tons |
For example, if you have a 4-ton air conditioning system, you need a furnace that can handle enough airflow. Since each ton of air conditioning requires about 400 CFM, a 4-ton system would need 400 CFM x 4 tons = 1600 CFM.
Therefore, for a 4-ton AC system, you should choose a furnace that provides at least 1600 CFM. You could choose a 1600 CFM or a 2000 CFM electric furnace based on the options listed.
Type of Electric Heating System
Here’s a simple breakdown of the five basic types of electric heating systems available in Canada:
- Forced-air Systems: These systems push heated air through ducts in your home. They can use electric resistance heating, heat pumps, or both to warm the air.
- Hydronic or Hot Water Systems: These use water heated by an electric boiler to warm your home. The hot water circulates through radiators or underfloor pipes to distribute heat.
- Room Heaters: Perfect for heating individual rooms or small spaces, these standalone units come in various styles and can be easily installed where needed.
- Radiant Systems: These provide heat directly from the floor, panels, or ceilings, offering a comfortable warmth without circulating air, ideal for reducing allergens.
- Combination Systems with Plenum Heaters: Installed in the hot air plenum of your central furnace, these systems add electric heating to your existing furnace.
Installation Location
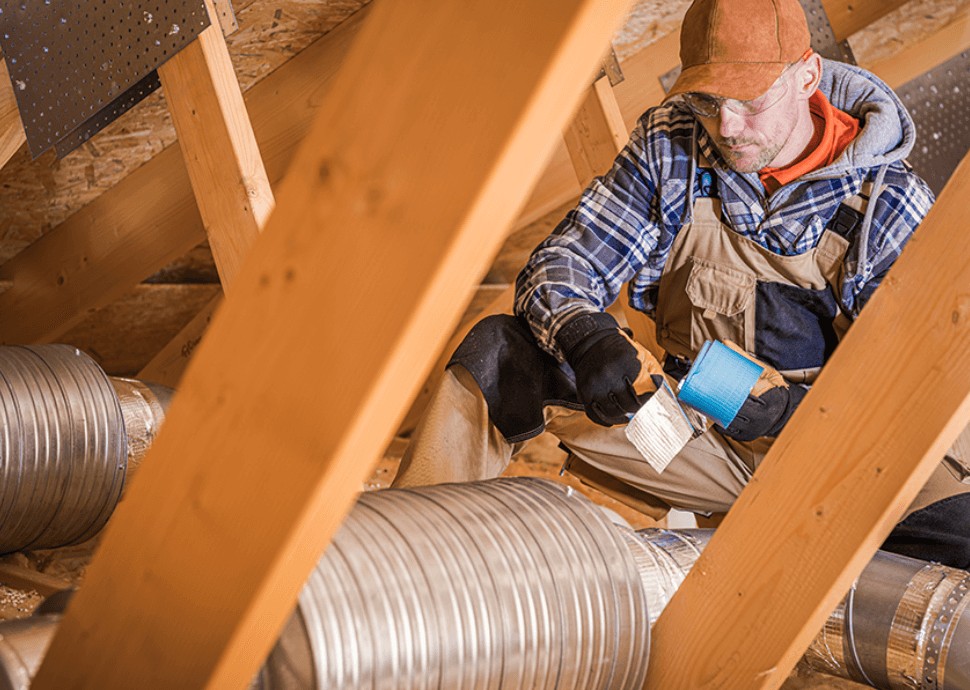

Ductwork installation is generally cheaper in attics and basements where access is easier, reducing hourly labor costs. Also, installing ducts in living areas often requires additional construction work, like removing and replacing drywall, increasing labor and material costs.
Get Quotes for Installing Electric Furnaces
Looking for a new electric furnace? Let us help make it easy. At FurnacePrices.ca, you can get free quotes from trusted local HVAC contractors. There’s no pressure to buy.
We check all our partners to ensure you get advice and quotes from the best. Just fill out a quick form and get the necessary information to choose the right furnace. Get free quotes today.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*










