Trying to figure out which HVAC heating system is the right one for your home can be confusing. With so many options available, it can be challenging to make the right choice.
This article will break down the two most popular HVAC heating systems: the reliable home heating furnace, and the modern cold climate heat pump. We’ll examine the pros and cons, compare them and answer a few questions about which one may be better for heating your home.
If you’re considering a heat pump, the federal and provincial governments may offer rebates and incentives for installing one.
Related:
What’s The Difference Between a Heat Pump and a Furnace?
Before we take a closer look at the pros and cons of each system, let’s find out how each of these heating systems works.
The Furnace Heating System
A furnace is one of the most popular ways to heat a home. Approximately 77 million furnaces are installed in households across North America. Furnaces heat a home using electricity, propane, natural gas, or oil. Several styles, brands, and types of furnaces are available on the market. A furnace does one thing – it heats your home with hot air.
In most cases, it does this by using a power source to ignite a burner located inside the furnace cabinet. Once the burners are lit, they heat a chamber. Then a blower fan sends air through the chamber where it picks up that heat and sends it through your ductwork and out the vents in your home to warm up the rooms.
An electric furnace works the same way, except it uses an electrically heated element instead of a burner, and the fan blows your air directly over it into the ducts.

With proper and regular cleaning of the filter and ducts, a furnace will provide 15 to 20 years of warm air in your home. Whether these systems are gas furnaces, electric furnaces, oil furnaces, or propane furnaces, they are all designed to generate heat during even the coldest winter temperatures.
The Heat Pump System
A heat pump works much differently than a furnace, and it can do more than simply warm a home. A heat pump can also work as an air conditioner, air filter, and dehumidifier. This one piece of technology can replace almost all the other HVAC equipment you would need for your home.
A heat pump can perform all these tasks efficiently because it doesn’t produce heat itself. Instead, it harvests and transports heat. During the winter, a heat pump takes heat from outside, concentrates it, then transports it throughout your home. During the summer, it reverses the process and draws heat energy from inside your house, and transports it outside.
Although it may sound like brand-new technology, it isn’t. The heat pump has been around for decades and uses the same technology found in refrigerators and air conditioners. Recently, innovative developments in heat pump technology have given them the ability to transport heat in and out of the home even when the temperatures are well below freezing outside.
Another selling feature of the heat pump is that it doesn’t necessarily require any of the standard ductwork a furnace does. Individual rooms or areas can be heated or cooled.
The most common heat pump for a home these days is an air-source heat pump. Geothermal systems are also available which takes heat from a water source or ground source to pump into your home.

When it comes to electricity usage, a heat pump uses much less power than a regular furnace. You’ll get 2x to 4x the amount of heat energy out of a heat pump vs electrical energy consumed.
The Pros and Cons of Heat Pumps and Furnaces
Each system comes with advantages and disadvantages. Let’s look at some things you can expect from each system.
The Advantages of Installing a Furnace
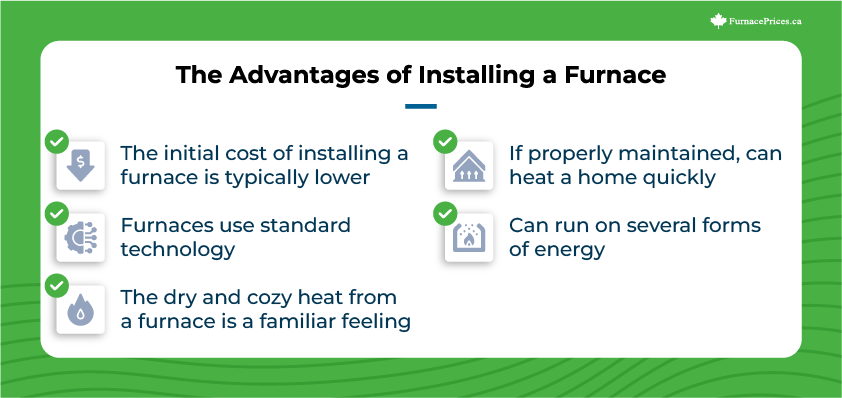
- The initial cost of installing a furnace is typically lower than installing a heat pump.
- Furnaces use standard technology that most technicians are familiar with.
- The dry and cozy heat from a furnace is also a familiar feeling most people are accustomed to.
- If properly maintained, a furnace can heat a home quickly.
- The furnace heat system can run on several forms of energy, such as natural gas, propane, oil, and electricity.
Even though furnaces are the most popular way to heat a home, they come with a few noticeable drawbacks.
The Disadvantages of Installing a Furnace

- A furnace, whether it’s a natural gas furnace, electric furnace, oil furnace, or propane furnace, uses much more energy than a heat pump system for a given output of heat – in some cases, three or more times as much.
- Installing a furnace means you will also have to install ductwork if you don’t already have some. This can be an expensive installation process, especially if the ductwork has to be retrofitted through the building frame.
- If your furnace is not properly cleaned and maintained, furnaces can malfunction prematurely.
- A furnace that is not correctly maintained and cleaned can also be a fire hazard.
- Furnaces don’t usually deliver a consistent temperature; they turn on and off multiple times a day.
- Whether you install a natural gas furnace, propane furnace, electric furnace, or oil furnace, the movement of hot air can introduce more airborne dust into your home.
- A furnace can only heat your home. You will have to install an air conditioner, dehumidifier, and air filter separately.
The Advantages of Installing a Cold Climate Heat Pump
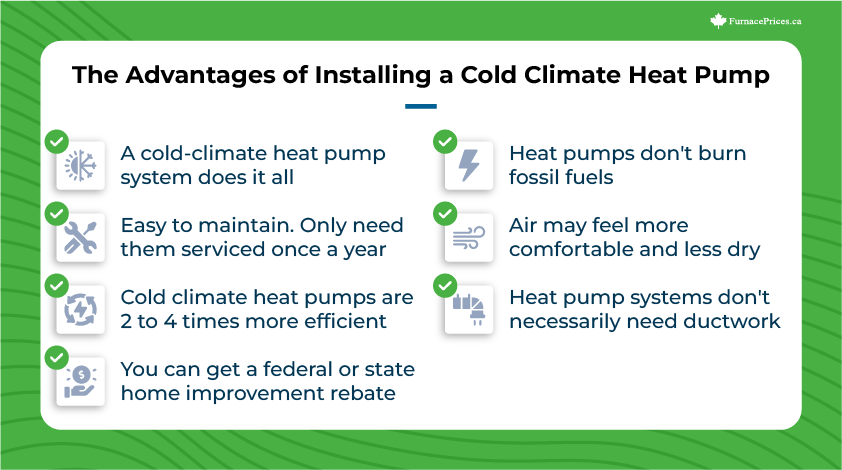
- A cold-climate heat pump system does it all. It cools, cleans, heats, and dehumidifies the air. You won’t need any other HVAC system installed.
- Heat pumps are easy to maintain, and you’ll only need them serviced once a year.
- Cold climate heat pumps are two to four times more efficient compared to any furnace.
- You can usually get a federal or state home improvement rebate when you install a heat pump.
- Heat pumps don’t burn fossil fuels like gas furnaces so they don’t pose any carbon monoxide risk to your home.
- The air that is circulated with heat pump systems may feel more comfortable and less dry than air heated by a furnace.
- Heat pump systems don’t necessarily need ductwork. This means fewer installation costs or retrofitting for older homes. They are available in several different styles that can even use existing ductwork and are available as mini-splits to heat or cool only one room or a few rooms.
Disadvantages of Installing Heat Pumps

- For those in colder climates, you may require a backup heating system to help during extremely cold weather. A cold climate heat pump can’t heat adequately if the outdoor air drops below -23ºC (-10ºF), and they are less efficient below -12° (10° F).
- The initial installation cost for a heat pump can be more expensive than a traditional furnace installation.
Heat Pump vs. Furnace: Things to Consider

Pros and cons aside, when choosing the right HVAC heating solution for your home, there are some things to consider. Let’s hone in on some of the things you should specifically look for with these heating systems and see if they fit your specific needs.
Choosing a Furnace
Most people leaning towards a specific type of furnace, like electric furnaces or gas furnaces, do so for several different reasons. Here are some things that might make you choose a furnace installation over a heat pump installation.
- You prefer to spend less on upfront installation costs.
- You want the bare bones in home heating systems.
- Your home already has air ducts and gas lines installed.
- You prefer and are prepared to keep a well-maintained furnace.
- You prefer a furnace’s heat over other heating systems like air-source heat pumps.
- You choose to install air conditioning separately or you already have AC.
- Your home doesn’t qualify for government assistance for the installation of a heat pump.
Choosing a Heat Pump
Cold climate heat pumps come as air-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps (drawing energy from a lake or river), or even geothermal heat pumps that draw heat from the ground.
All heat pumps are 200% to 300% more efficient than an electric furnace. Here are some other reasons people choose a heat pump over a furnace:
- Although more expensive upfront than a furnace, government rebate programs may cover a heat pump installation.
- You prefer all of your climate control, heating, cooling, filtering, and dehumidifying to be done by one piece of equipment.
- You understand the costs associated with using a gas furnace or heating oil and the possible problems related to a furnace that can produce carbon monoxide.
- Your home does not have existing ductwork or is not designed for ductwork installation.
- You have an older home that requires unique heating needs to heat the house evenly.
- You like the idea of room-by-room temperature control if you use mini-split systems. And even heat one room while cooling another.
- You want a low-maintenance heating system.
Heat Pump vs. Furnace FAQs
Are you still wondering about the great furnace debate of heat pump vs. furnace? To help you with your decision, let’s look at the most common questions people have about these two different heating systems.
Are Electric Furnaces a Good Option?
Yes, electric furnace systems are a good choice for many homeowners. They require minimal upfront installation costs, but these systems are less energy efficient than other heating systems.
So if you’re looking for better energy efficiency, there are definitely better options than an electric furnace.
Do You Need a Dual Fuel System With a Heat Pump?
You won’t need supplemental heating systems like a gas or electric furnace with heat pumps for mild winter temperatures.
Heat pumps work by harvesting heat energy from the outside air. However, in super cold climates where the outdoor temperature drops below -23ºC (-10ºF), an air source heat pump may need an additional (typically) electric heater installed as a backup.
Do Heat Pumps Need Gas to Work?
No. Heat pumps run on electricity only and don’t directly use fossil fuels like gas, propane, or oil. In the debate over a heat pump vs. a furnace when it comes to direct fossil fuel use, heat pumps win even if the electricity is generated with fossil fuels.
Oil, propane, or gas furnaces can leak carbon monoxide if not properly maintained. It’s always important to have your oil, propane, or gas furnace inspected and maintained regularly.
Heat Pump vs. Gas Furnace: Which One is Cheaper to Run?
In most cases, heat pumps are cheaper to run than gas furnaces. However, depending on what province you live in, energy costs can vary drastically.
Generally speaking, heat pumps can be up to four times more energy efficient than a gas furnace. The energy efficiency of heat pumps means that you’ll be cutting down on your home’s energy waste quicker than you would with a gas furnace.
Do You Need an Air Conditioner With Heat Pumps?
No. The heat pump’s indoor and outdoor units can keep your home warm during winter and also cool during the summer. During the summer months or in warmer climates, the indoor unit cools off and circulates the hot indoor air, which quickly cools the home.
And during the winter, the outdoor unit generates its own heat source by drawing any heat from the outside and transferring it to the home’s indoor air. An additional air conditioning unit is not needed.
Heat Pump vs. Furnace: Which One is the Noisiest?
Heat pumps are quiet systems. Gas furnaces use heat exchangers that can expand and contract, along with the ductwork, making noises. Heat pumps are a better choice if you like a particularly quiet home.
However, there are some very quiet gas furnaces on the market if you need a more cost-effective option that can be almost as quiet.
Can You Replace a Heat Pump With a Furnace?
Yes! You can replace traditional gas furnaces or electric furnaces with a heat pump, but the other way might not work as easily. Heat pumps can be installed in a home regardless if there is existing ductwork or not.
However, if the home doesn’t have any existing ductwork and you want to install a gas furnace, you will also have to install ductwork – which is a very large extra cost. Installing fuel lines can also be expensive. Before installing a gas furnace or a heat pump, look at your home’s features and layout.
This will determine if gas furnaces or heat pumps will work best with your home’s design.
Heat Pump vs. Furnace: Final Thoughts
Installing any HVAC system requires careful planning and decision-making. Are you looking for better heating efficiency or reducing heating costs? Do you like the idea of heat energy drawn from the outside with heat pumps?
Or do you prefer a traditional indoor unit like a gas furnace? Are you concerned about the air quality? And is your home designed to accommodate ductwork installation?
Asking a few simple questions like these will determine which type of heat system will be better suited for your home. Ultimately, the decision to heat your home will be based on many factors, such as budget, heat energy, style, and personal preference.
Talk to a local HVAC specialist for more information on these heating options.
Get Quotes
How soon are you looking to buy?*